Power Transformer
A power transformer is a type of electrical transformer used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction, typically at high voltage levels. Unlike distribution transformers, power transformers are used mainly in transmission networks to step up or step down voltage levels for efficient long-distance power transmission.
Main Functions
- Step-up Transformer: Raises voltage from a power plant for transmission.
- Step-down Transformer: Lowers voltage at a substation before distribution.
- Handles Large Loads: Typically operates above 33 kV and has ratings from 100 MVA and higher.
Key Components
- Core: Laminated steel core to carry magnetic flux.
- Windings: High-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) windings made of copper or aluminum.
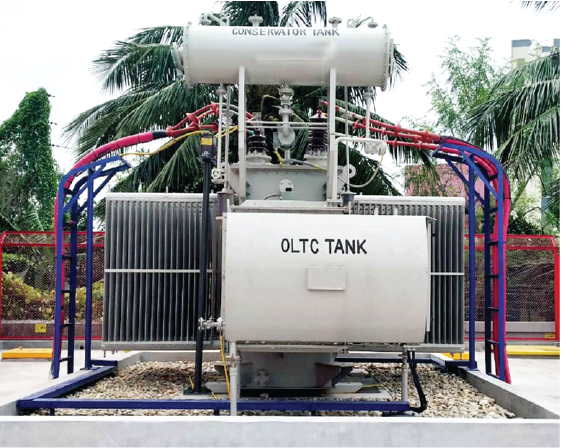
- Tank: Steel tank filled with insulating oil for cooling and insulation.
- Radiators: Dissipate heat generated during operation.
- Buchholz Relay: Detects gas buildup due to internal faults.
- Tap Changer: Adjusts output voltage to regulate power delivery.
Typical Specifications
- Voltage Levels: 400 kV / 220 kV / 132 kV / 66 kV
- Power Ratings: 100 MVA to 1000 MVA or more
- Phase: Three-phase (most common in transmission systems)
- Cooling: ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural), ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced), OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced), etc.