Distribution Transformer
A distribution transformer is an essential component of the electrical power distribution system. Its primary role is to step down the high voltage from the transmission lines to a lower voltage suitable for use in homes, commercial buildings, and small industries.
Key Functions
• Voltage Conversion: Converts high transmission voltage
(e.g., 11 kV or 33 kV) to a lower voltage (e.g., 230V or 400V).
• Load Distribution: Supplies electrical power to end-users over
short distances.
• Efficiency: Designed for high efficiency and low losses during operation.
Types of Distribution Transformers
1. Pole-Mounted – Mounted on electric poles; common in rural and suburban areas.
2. Pad-Mounted – Ground-mounted, enclosed in a locked steel cabinet; used in urban areas.
3. Underground – Installed below ground level for compact urban settings.
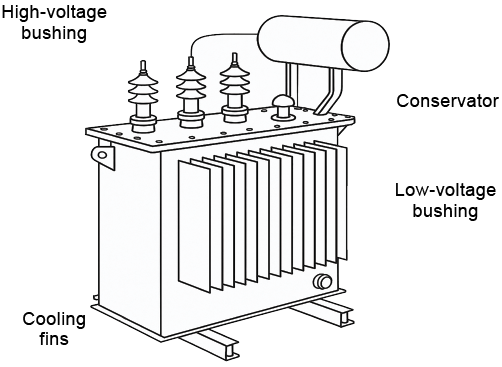
Construction Features
• Core: Made of laminated silicon steel to minimize
energy losses.
• Windings: Copper or aluminum conductors wound
around the core.
• Tank: Contains insulating oil (in oil-filled transformers)
that cools and insulates.
• Bushings: Insulated terminals for input (high voltage)
and output (low voltage) connections.
Safety & Maintenance
• Equipped with protection devices like fuses, surge
arresters, and circuit breakers.
• Regular maintenance includes checking oil levels,
insulation resistance, and overheating.