Solar System
A solar system is a renewable energy setup that uses sunlight to generate electricity or heat. The most common system is the solar photovoltaic (PV) system, which converts sunlight directly into electrical energy using solar panels. It is a clean, eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuel-based energy sources and helps reduce carbon emissions. components for load management, fault isolation, and system protection. MDBs are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial installations to organize and manage electrical power distribution efficiently and safely.
Types of Solar Systems
• On-Grid Solar System
• Connected to the main electricity grid.
• Surplus power is exported to the grid (net metering).
• No battery storage required.
• Ideal for urban homes, offices, and factories.
• Off-Grid Solar System
• Works independently from the grid.
• Requires battery storage to store excess energy.
• Suitable for remote areas with no grid access.
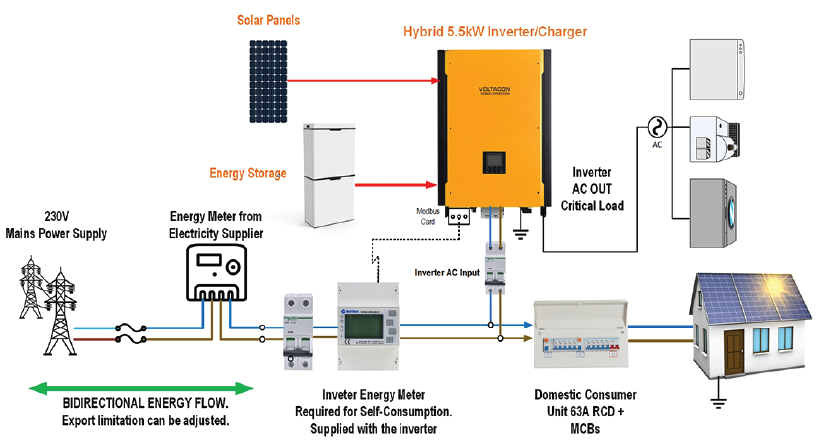
• Hybrid Solar System
• Combines both on-grid connection and battery storage.
• Ensures power backup during outages.
• Useful for locations with unreliable grid supply.
Uses of Solar Systems in Different Fields
1. Residential – Power for homes, lighting, and appliances
2. Commercial – Offices, malls, and institutions reduce electricity costs
3. Industrial – Supports energy-intensive processes and operations
4. Agriculture – Powers irrigation pumps, dryers, and cold storage
5. Public Utilities – Street lighting, traffic signals, solar-powered CCTV
6. Remote Areas – Provides electricity where grid power is unavailable
7. Educational and Healthcare – Ensures uninterrupted power for labs, hospitals, and schools
Benefits of Solar Systems
• Reduces electricity bills
• Low maintenance
• Environmentally friendly
• Energy independence
• Long lifespan (25+ years for panels)